In Depth
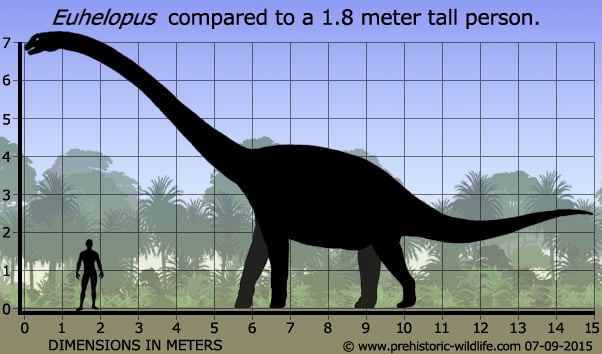
Euhelopus was originally named Helopus until it was discovered that the name had already been used for a bird. The name was altered to Euhelopus by Alfred Romer in 1956. Euhelopus was similar to the macronarian sauropods in that the fore legs were proportionately longer than the rear legs, something that would have resulted in a posteriorly sloping back. This might have allowed Euhelopus extra reach, but the height that sauropods carried their heads is a matter on contention for some palaeontologists.
Further Reading
– Osteology of the Reptiles. – University of Chicago Press 1-772. – A. S. Romer – 1956. – Redescription and reassessment of the phylogenetic affinities of Euhelopus zdanskyi (Dinosauria:Sauropoda) from the Early Cretaceous of China. – Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 7 (2): 199–239. – Jeffrey A. Wilson & Paul Upchurch – 2009. – Photographic Atlas and Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Holotype Skull of Euhelopus zdanskyi with Description of Additional Cranial Elements. – PLOS ONE. 8 (11): e79932. – Stephen F. Poropat & Benjamin P. Kear – 2013.