In Depth
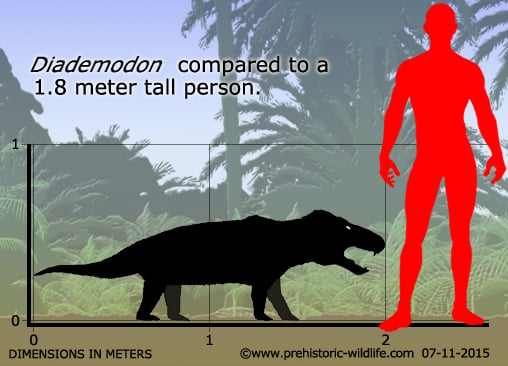
The cynodonts are known to come in a variety of sizes, but at up to two meters in length, Diademodon is easily amongst the largest known cynodonts. Like other cynodonts, Diademodon may have been an omnivore eating both certain parts of plants as well as other animals and carrion. Diademodon lived during the early Triassic, and most of the known fossils are known frim Africa. However, fossils attributed to Diademodon have now also been located in South America and Antarctica, further suggesting that as a genus Diademodon became very successful and widespread.
Further Reading
- The palaeoecology of the non-mammalian cynodonts Diademodon and Cynognathus from the Karoo Basin of South Africa, using stable light isotope analysis. - Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 223 (3–4): 303. - J. Botha, J. Lee-Thorp & A. Chinsamy - 2005. - Diademodon tetragonus Seeley, 1894 (Therapsida: Cynodontia) in the Triassic of South America and its biostratigraphic implications. - Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 29 (3): 852. - A. N. G. Martinelli, M. D. L. Fuente & F. Abdala - 2009.